Code 401 Class 02 Reading Notes
In Tests We Trust - TDD with Python
TDD(Test-Drive Development) “Clean code that works (Ron Jeffries)” - is the goal of Test-Driven Development. (preface, p.ix)
~ Stanislav Pankevich’s blog
- Unit tests are some pieces of code to exercise the input, the output and the behavior of your code.
Important aspects about the unit test
- Test Name : This needs to be descriptive and say what is expected and what is being tested.
- Test File Name : Should follow the same name of module name. If the module is
name.py, the test name should betest_name.py. These should be kept in separate folders.
mymodule/
- module.py
- another_folder/
- - another-module.py
tests/
-test_module.py
- another_folder/
- - test_another_module.py
- Structure : A popular convention is the AAA: Arrange, Act, and Assert.
- Arrange: Data needs to be organized to execute that piece of code(input);
- Act : here you will execute the code being tested(exercise);
- Assert : After executing the code, you will check if the result (output) is the same as you were expecting.
Finally, add lib pytest, if you are so inclined.
The Cycle
- Write a unit test and make it fail (it needs to fail because the feature isn’t there)
- Write the feature and make the test pass.
- Refactor the code - the first version doesn’t need to be the beautiful one.
Don’t think about the feature, think about the test.
TDD is not about the money/tests
More than any checking, we need to think about our software design first.
If name equals main
Every Python module has it’s __name__ defined and if this is __main__, it implies that the module is being run standalone by the user and we can do corresponding appropriate actions.
If you import this script as a module in another script, the __name__ is set to the name of the script/module.
Python files can act as either reusable modules, or as standalone programs.
If __name__==”main”: is used to execute some code only if the file was run directly, and not imported.
Recursion
Recursion: The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the corresponding function is called as recursive function. Using recursive algorithm, certain problems can be solved quite easily.
A mathematical Interpretation
approach(1)-Simply adding one by one
f(n)=1+2+3+.....+n
Another mathematical approach
approach(2)-Recursive adding
f(n)=1 n=1
f(n)=n+f(n-1) n>1
The difference between approach(1) and approach(2) is f() itself is being called inside the function, so this phenomenon is named as recursion and the function containing recursion is called recursive function.
What is base condition in recursion?
The solution to the base case is provided and the solution of the bigger problem is expressed in terms of smaller problems.
int fact(int n)
{
if (n < = 1) // base case
return 1;
else
return n*fact(n-1);
}
Base case for n<=1 is defined and larger value of number can be solved by converting to smaller one till base case is reached.
How a particular problem is solved using recursion?
The idea is to represent a problem in terms of one or more smaller problems, and add one or more base conditions that stop the recursion. For example, we compute factorial n if we know factorial of (n-1). The base case for factorial would be n=0. We return 1 when n=0.
Why Stack Overflow error occurs in recursion?
If base case is not reached or not defined, the the stack overflow problem may arise.
int fact(int n)
{
// wrong base case it may case
// stack overflow.
if (n == 100)
return 1;
else
return n*fact(n-1);
}
What is the difference between direct and indirect recursion?
// An example of direct recursion
void directRecFun()
{
// Some code....
directRecFun();
// Some code...
}
// An example of indirect recursion
void indirectRecFun1()
{
// Some code...
indirectRecFun2();
// Some code...
}
void indirectRecFun2()
{
// Some code...
indirectRecFun1();
// Some code...
}
A function fun is called direct recursive if it calls said function fun. A function fun is called indirect recursive if it calls another_function and another_function calls fun directly or indirectly.
What is difference between tailed and non-tailed recursion?
A recursive function is tail recursive when recursive call is the last thing executed by the function.
How memory is allocated to different function calls in recursion?
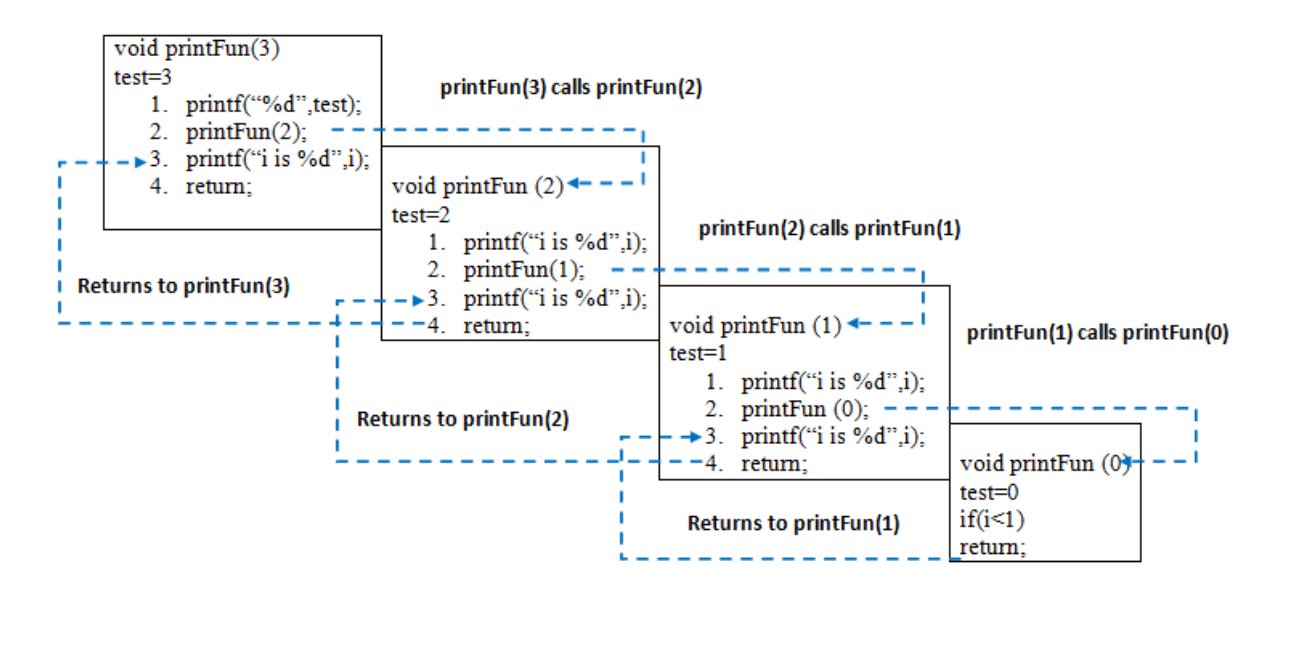
When printFun(3) is called from main(), memory is allocated to printFun(3) and a local variable test is initialized to 3 and statement 1 to 4 are pushed on the stack as shone in below diagram. It first prints ‘3’. In statement 2, printFun(2) is called an memory is allocated to printFun(2) and a local variable test is initialized to 2 and statement 1 to 4 are pushed in the stack. Similarly, printFun(2) calls printFun(1) and printFun(1) calls printFun(0). printFun(0) goes to if statement and it return to printFun(1). Remaining statements of printFun(1) are executed and it returns to printFun(2) and so on. In the output, value from 3 to 1 are printed and then 1 to 3 are printed.
What are the disadvantages of recursive programming over iterative programming?
Every recursive program can be written iteratively and vice versa is also true. The recursive program has greater space requirements than iterative program as all functions will remain in the stack until the base case is reached. It also has greater time requirements because of function calls and returns overhead.
What are the advantages of recursive programming over iterative programming?
Recursion provides a clean and simple way to write code. With iterative programming, we would need the help of a stack data structure.
What on Earth is Recursion
An example
factorial(n)=n*factorial(n -1)
Endless of things defined within themselves.
Factorial is completed in the computer is done Recursively.
The factorial of the number below, so you have to go through the function again. Until you reach zero. Factorial does not go to negatives.
The main program will be working through a factorial that you set, say 4, and will stack a factorial 4 on top of that main program. Then it will want to know what factorial 3 is, so factorial 3 is stacked on top. Till we hit 1 at the very top. Then, once that is complete, 1 is multiplied by the below factorial, which is 2. So now we have a multiplier of 2, to multiply the below stack ,3, which is 6. Then, multiply 6 to the below stack, at the main program, which is 4, which will equal 24. And then the program stops.
Things I want to know more about
What are the most common ways to create stack overflow in recursion.